Holy shit – did you know that 750,000 Americans have their gallbladder surgically removed every year?
OK, I needed to look this up and oops, I was wrong 😅
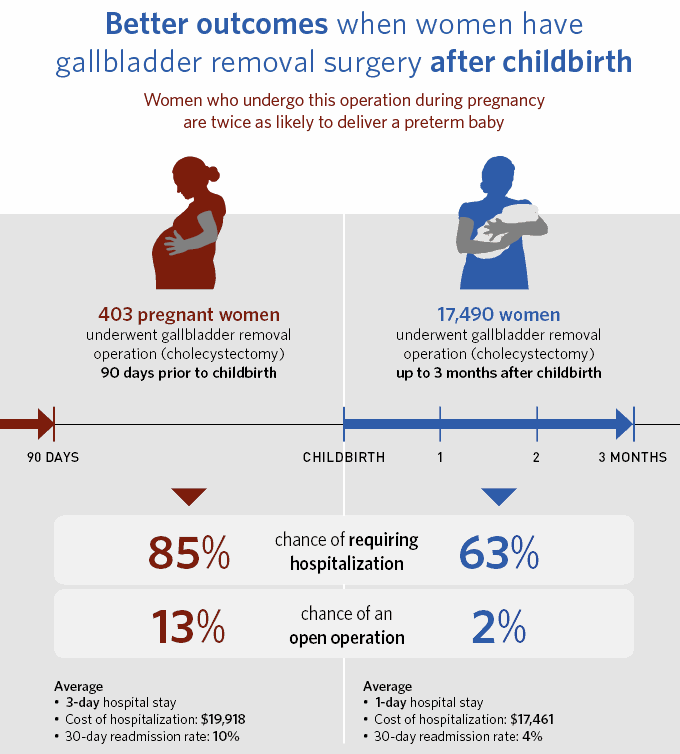
Gallbladder removal, also known as cholecystectomy, is one of the most common procedures in the United States, with more than 1.2 million cholecystectomies done annually. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448176/
When it comes to dry fasting something that needs to be taken into consideration more so than anything else is the risk of gallstones. With water fasting it's a bit less of a concern because you are not dehydrating the body and therefore you are not dehydrating your bile. Water fasting also has an inherent mechanism to lower cholesterol saturation in the bile. Have I scared you off of dry fasting? Good. You should be scared. It's the most powerful form of healing – It is a MIRACLE MAKER – but it should never be taken lightly.
It blows my mind how many people think they understand the liver, gallbladder, and gallstone connection. The recommendations are all over the place. It's as if no one is making the right connections, and the loudest people are the ones who have never had a chronic illness or problems with their liver. True knowledge comes from the blending of science with personal experience.
TLDR
- Dietary cholesterol (meat and animal products) does not mix well with [carbs and seed] oils.
- It is easier and less dangerous to go from a high-carb low-fat diet (HCLF) to a high-fat low-carb (HFLC) diet due to bile pool size and bile flow increase.
- It is very important to have a liver strategy in between fasting windows.
- Coconut is nature's best fat source for liver health.

Extra Readings on the Science Behind Liver Flushing:

Extra Readings on different ideas for Liver Flushing:

Medical professionals are often clueless when it comes to the gallbladder, diet, and fasting
Doctors go through school, memorize a metric ton of information for tests, and then forget 90% of it later on. That, or they just get desensitized and bored. You've all heard the saying that doctors spend less than a few hours focusing on nutrition. But then someone pipes up and says: "WeLL yoU sHoulD aLso tAlK tO a NutRiTionIst!!" Sorry, but most nutritionists I've talked to are often even more clueless. A quote comes to mind.
It is difficult to get a man to understand something when his salary depends upon his not understanding it.
So the common recommendation nowadays is to try to minimize the pain by eating no fat, and eventually have surgery. Doctors don't discuss any other alternatives. They tell you to: "Adopt a low-fat diet to reduce gallstone formation and alleviate symptoms." The only reason this has any credence is the fact that if you are still consuming processed foods + dietary cholesterol which is often found in a high-fat diet, THEN you are in more trouble.
Maybe if you push them hard enough they'll mention Ursodeoxycholic acid (then they'll say that it may take years, and most likely won't work). They might also tell you (if pushed harder) that you can do Shock Wave Lithotripsy which uses sound waves to break up gallstones into smaller pieces. What's the problem with this? If you've got stones, you'll most likely keep getting them unless you start to truly UNDERSTAND them.
Telling people not to eat fat when they have stones is the equivalent of FORCING them to eventually get surgery. No wonder the numbers are astronomical. Now, don't get carried away. If you're already severe and have massive stones, they might take you out and force you to have to get it removed ASAP. Excruciating pain and chronic is a serious problem. If you have to get your gallbladder removed, you'll just have to learn to live with it, but if you're still unsure if you NEED to get it removed, don't let a bunch of sycophants persuade you that you don't need it and that you should join their club.
Effects of Fasting on Bile Acid Metabolism
Ok, let's take a little break and jump into some studies. This is a very important study whose concepts I've used successfully with others and when some of my experiments had gone wrong. This study provides the proof that some of you need to even consider trying this. A lot of people

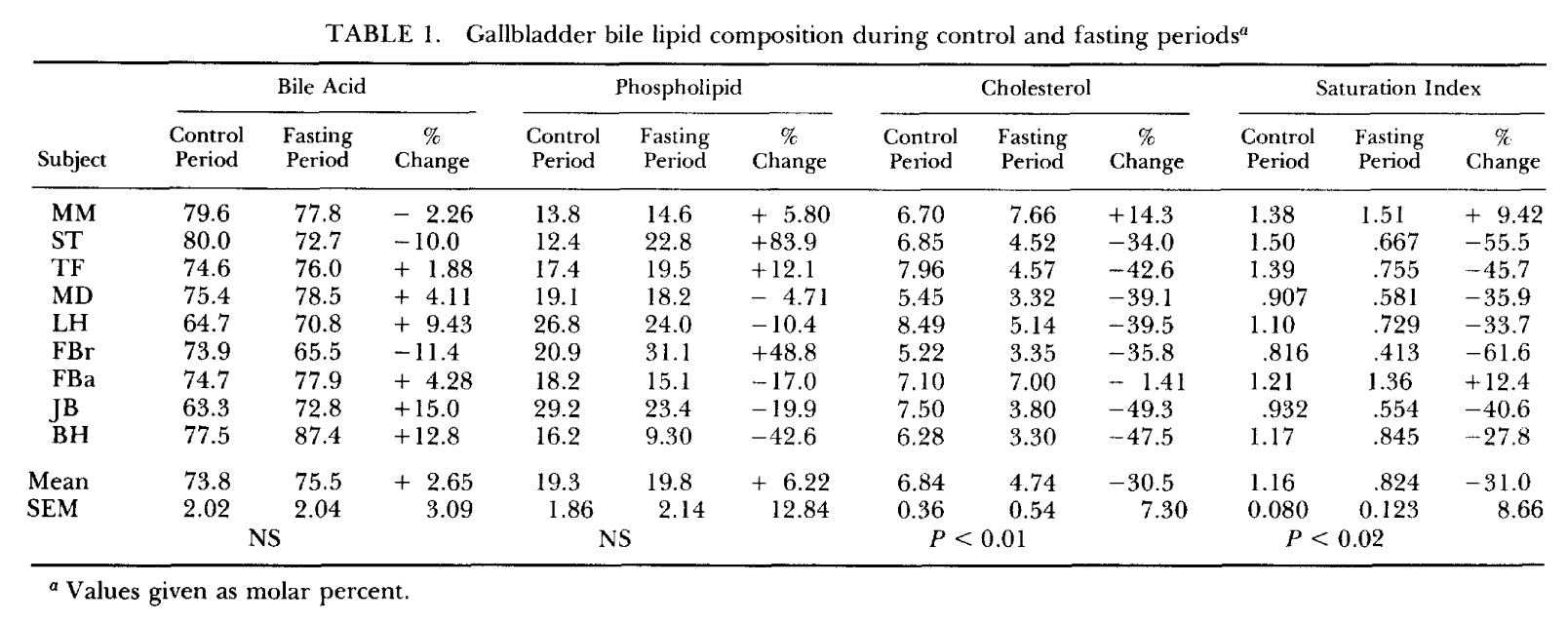
A 4-6 day fast reduces the molar percent of the cholesterol in gallbladder bile, unlike short fasts (12 hours) which increase it.
This correlates to another study - Effects of Fasting on the Composition of Gallbladder Bile - which I talk about in a little bit.
8 out of 9 subjects showed a greater than 30% reduction in cholesterol molar percent by the fourth day of fasting.
A good baseline to work by when attempting to lower cholesterol.
The Mechanism seems to be that the reduced hepatic cholesterol synthesis and absence of dietary cholesterol during fasting may reduce cholesterol secretion into bile.
I would also add that the inhibition of bile acid reuptake in the ileum plays a role as well. Around the 16-hour mark of fasting the body's reuptake mechanisms get suppressed (look into my bile acid and fasting post from before). This explains why a liver flush experience requires some form of fasting for full benefits.
Some other studies, like those on Rhesus monkeys, suggest intermittent fasting increases cholesterol content, but prolonged fasting may reduce it.
Most other studies focus on short intermittent fasting which may actually make gallstones worse.
Reduced caloric intake with some food doesn't simulate complete fasting effects on bile composition.
As much as you would like to believe that you can simply do a fast-mimicking diet to get these results, it doesn't work that way. Proper complete water fasting is what was measured and most effective. Yes, there's room to experiment with things like freshly squeezed lemon water during these fasts, which may add another element of healing.
Effects of Fasting on the Composition of Gallbladder Bile
This is an important study that highlights the dangers of constant intermittent fasting when dealing with a sick liver or a diet low in bile flow. Constantly doing a 16:8 hour IF will keep putting you into that higher cholesterol saturation window and initiate cholesterol precipitation into gallstones. But get past 36 hours of water fasting and you start to enter negative saturation territory that starts to shrink stones.

- 15-Hour Fast Increases Cholesterol Saturation
- 20-Hour Fast Reduces Cholesterol Saturation
- The total biliary lipid concentration remains unaffected by short fasting duration (under 24hrs)
Top 10 Reasons Someone Might Have Gotten Gallstones:
- High Cholesterol Levels: Excess cholesterol in bile can form crystals that lead to gallstones.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the amount of cholesterol in bile, contributing to gallstone formation as well as increased estrogen. Aromatase connection including insulin resistance.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Quick weight loss can cause the liver to secrete extra cholesterol into bile.
- Diabetes: Higher triglyceride levels in people with diabetes can increase the risk of gallstones. Most commonly seen in the obese.
- Diet: High-fat, high-cholesterol, and low-fiber diets can contribute to the formation of gallstones.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men, particularly during pregnancy or when taking hormone replacement therapy. This is the link to Estrogen. Estrogen is also elevated in FAT MEN and WOMEN due to aromatase in the fat cells that converts androgens to estrogens.
- Age: People over 40 are at higher risk for gallstones.
- Family History: Genetics can play a role; a family history of gallstones increases your risk.
- Certain Medications: Medications like cholesterol-lowering drugs and birth control pills can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Gallbladder Disease: Conditions that affect gallbladder function, such as biliary sludge or reduced gallbladder motility, [OFTEN A RESULT OF CHRONIC ILLNESS] can lead to gallstone formation.
What to eat when you think you've got gallbladder issues?
This advice comes from what I would personally do or have done in the past. I've tested different diets, different approaches, and different ways of fasting. It's true when they say that everyone is unique because so many factors come into play when considering an approach tailored to you.
- Consider transitioning into a diet like a high-fat keto diet
- Add in apple cider vinegar before meals (lowers cholesterol synthesis)
- Consider water fasting for at least 3 days
- Consider doing an apple (green) and coconut diet
- Incorporate lemon water as much as possible
- Strategically liver flush if it makes sense for your situation
- TUDCA/Ox bile helps specifically when the liver is not producing enough bile salts. Hard to know for sure, but if you don't get any digestive relief when taking bile salts (up to a few weeks) it's usually an indicator that you don't need them and the issue lies in cholesterol/bilirubin.
Lemons
Lemon pectin can help prevent gallstones by stopping bile acids from being reabsorbed in the gut, while lemon juice encourages the gall bladder to contract and flush out bile and small gallstones. For a thorough gall bladder flush, drink 4 cups of apple juice daily for six days, then on the seventh day, take 2 tablespoons of Epsom salts in water, wait an hour, and consume 1/2 cup of olive oil with 4 tablespoons of lemon juice. Lie on your left side for 30 minutes before sleeping. Alternatively, a less extreme method involves taking 1 tablespoon of lemon juice mixed with 1 tablespoon of olive oil an hour before breakfast daily, which can help break down and expel gallstones by encouraging gall bladder contraction.
Eat more saturated fat (keto) but be mindful of caloric surplus
This is why I always advise a keto diet to get rid of gallstones – It just works. You increase your bile pool size, you increase your bile flow, and you shift your gut microbiome to an increase in bacteria that are dedicated to gallbladder health. In dire situations, this is the solution. You can even turn towards a vegetarian-style keto that focuses heavily on coconut (notice the saturated fat requirement). Avocados and Olive oil won't increase your bile pool size much, but they will help with bile flow and allow for a bit more variety in the diet. I'd also mix in apples and lemons. Women = higher estrogen = more prone to gallstones due to lower motility and higher cholesterol creation.
Mixing Polyunsaturated with Dietary Cholesterol is a recipe for Gallstones

Peanut butter is exactly what we don't want - super unbalanced high levels of omega 6 which is linked to gallstone formation especially when in the present on dietary cholesterol. Higher protein diets almost always include dietary cholesterol due to animal products.


Ok, let's break it down.
Cholelithiasis (gallstone) Incidence
- Safflower oil group: 9 out of 10 monkeys developed cholelithiasis.
- Butter group: 3 out of 7 monkeys developed cholelithiasis.
- Coconut oil group: 1 out of 7 monkeys developed cholelithiasis.
- Control group: No monkeys developed gallstones.
Bile Acid Pool Expansion
- Butter- and coconut oil-fed groups had significantly expanded bile acid pools compared to controls (p < 0.05).
- Butter-fed group had a significantly increased cholic acid fractional catabolic rate (p < 0.05).
Safflower Oil Group Findings
- Had the smallest mean bile acid pool.
- Had the highest mean lithogenic index among cholesterol-fed groups.
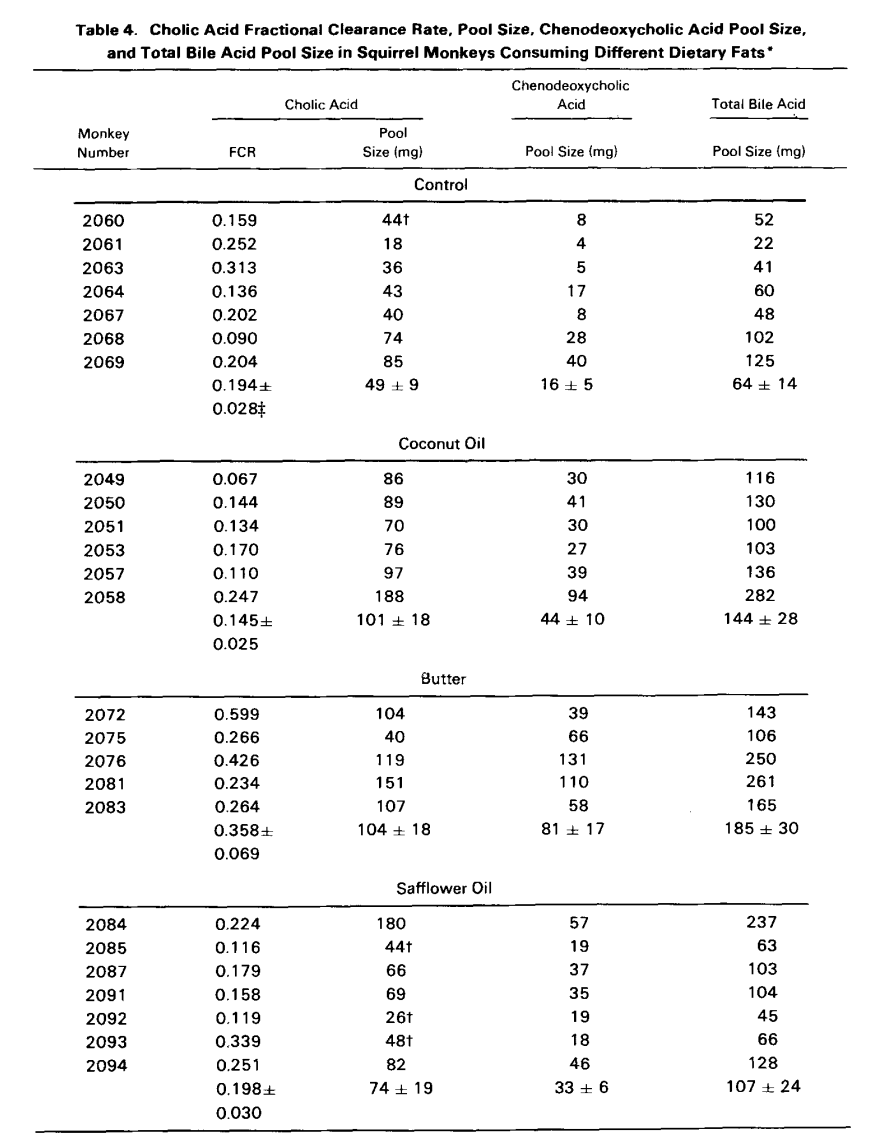
OK Now Their Conclusions
- Safflower oil-fed animals had a higher incidence of cholelithiasis because they did not stimulate bile acid synthesis to compensate for high cholesterol intake.
- Coconut oil-fed animals likely absorbed less cholesterol, preventing bile saturation with cholesterol. Only one monkey developed stones, and upon further inspection, the stones were not cholesterol stones - indicating a different mechanism and possible genetic factor with the one monkey.
FAQs
Is Fasting Good for Gallbladder Problems? Yes, fasting can benefit gallbladder health by promoting liver function and reducing inflammation. However, prolonged fasting may cause temporary discomfort due to increased cholesterol levels and bile sludge formation. Combining intermittent fasting with a ketogenic diet can provide long-term benefits in improving digestion.
Can Fasting Trigger Gallbladder Pain? Fasting may temporarily trigger gallbladder pain in some individuals, especially those with preexisting conditions or susceptibilities. This is usually caused by the release of triglycerides during fasting and subsequent increases in cholesterol levels, which can lead to bile sludge formation.
Does Fasting Cause Gallbladder Sludge? Fasting might contribute to the formation of bile sludge due to increased cholesterol production resulting from triglyceride release. Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome and supporting liver function through dietary choices like the ketogenic diet can help prevent complications related to bile sludge.
Does Not Eating Make the Gallbladder Worse? Not eating for an extended period could worsen existing gallbladder issues by increasing cholesterol levels and causing bile stasis. It's essential to maintain a healthy balance between periods of eating and fasting while ensuring proper nutrition intake when following any dietary plan involving calorie restriction or time-restricted feeding patterns.
How Can a Ketogenic Diet Support Gallbladder Health? A ketogenic diet supports gallbladder health by encouraging the body to use fat as its primary fuel source, reducing bile stasis, and promoting regular bile flow. By minimizing carbohydrate intake and focusing on healthy fats, the ketogenic diet can help prevent gallstone formation and improve overall gallbladder function.
What Are the Signs of Gallbladder Issues? Signs of gallbladder issues include gastric inflammation, tenderness in the right shoulder area, and strain beneath the lower right rib cage. These symptoms can indicate an increased risk of gallstone formation and other gallbladder-related problems.
How Long Does It Take for Gallbladder Symptoms to Improve on a Ketogenic Diet? Gallbladder symptoms may initially worsen during the early phases of keto-adaptation as the body adjusts to burning fat for fuel. However, these symptoms typically improve within a few weeks as the body becomes more efficient at utilizing fat, and bile flow normalizes. Mixing in green apples can speed this up too.
Extras
A few things I quickly ran across and didn't want to go too deeply on.
Ivermectin
Another reason why Ivermectin (a FXR agonist) may help chronically ill people.
Gallstone Disease and Its Correlation With Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism: Extra cholesterol because the body gets weaker and slower and panics.
Hyperthyroidism: Too much cholesterol is formed as the body goes into hypermetabolic mode.

What most naturopaths don't understand is that hyperthyroidism is just as dangerous if not MORE dangerous than hypothyroidism. I've talked to a few who believed that only hypothyroidism puts you at risk of gallstones. It just shows how few people out there truly try to understand the connections.
Hyperthyroidism and Gallstones
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can cause cholesterol gallstones by affecting certain genes in the liver (Lxrα and Rxr) that control how cholesterol is processed and used in the body.
Hypothyroidism and Gallstones
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) leads to cholesterol gallstones by increasing the production of cholesterol in the body.
I lived both hypothyroidism through long covid and low-carb diets. And I lived through hyperthyroidism when switching to high-carb diets. There are many traps and I could write a book about it, but just thinking about that makes me exhausted, pun intended.
Good luck on your dry fasting journey.


